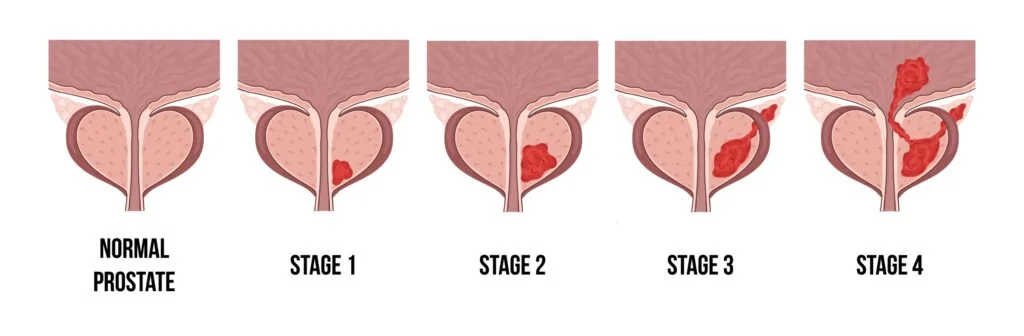
Prostate cancer, a malignant growth in the prostate gland, represents a significant health concern for men worldwide. While it often develops slowly and may not initially cause noticeable symptoms, prostate cancer can be aggressive and life-threatening if left untreated. Understanding the dangers associated with prostate is crucial for early detection, diagnosis, and effective treatment. Let’s explore the risks and implications of this insidious disease.
Prostate Cancer
Silent Progression:
One of the most insidious aspects of prostate cancer is its tendency to progress silently, often without causing noticeable symptoms in its early stages. As a result, many men may remain unaware of the presence of prostate until it has advanced to a more advanced stage or spread to other parts of the body. Regular screening and proactive monitoring are essential for detecting prostate cancer at its earliest and most treatable stages.
Risk Factors:
Several factors may increase an individual’s risk of developing prostate cancer, including age, family history, race, and lifestyle factors. Men over the age of 50, those with a family history of prostate, and individuals of African American descent are at higher risk. Additionally, factors such as obesity, poor diet, smoking, and sedentary lifestyle may contribute to an increased risk of developing prostate cancer.
Symptoms and Warning Signs:
While prostate cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages, as the disease progresses, it may manifest symptoms such as difficulty urinating, weak or interrupted urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, and bone pain. Any persistent or concerning symptoms should prompt a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Complications and Health Impacts:
If left untreated, prostate cancer can lead to serious complications and health impacts, including metastasis (spread) to other organs and tissues, such as the bones, lymph nodes, and distant organs. Metastatic prostate cancer is more challenging to treat and may result in significant pain, disability, and reduced quality of life. Additionally, advanced prostate may increase the risk of complications such as urinary obstruction, bone fractures, and spinal cord compression.

Prostate Cancer
Treatment Challenges:
Treating prostate cancer presents unique challenges, particularly in cases where the disease has advanced or metastasized. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy, depending on the stage, aggressiveness, and characteristics of the cancer. Each treatment modality carries potential risks, side effects, and considerations that must be carefully weighed and discussed with a healthcare provider.
Importance of Early Detection and Screening:
Early detection is critical for effectively managing prostate cancer and improving treatment outcomes. Men should undergo regular screening for prostate cancer, typically through a combination of a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. Screening guidelines may vary based on individual risk factors and recommendations from healthcare professionals.
Prostate cancer poses a significant threat to men’s health, with the potential for serious complications and adverse outcomes if left untreated. Understanding the risks, symptoms, and implications of prostate is essential for early detection, diagnosis, and appropriate management. By raising awareness, promoting regular screening, and advocating for proactive healthcare, we can reduce the impact of prostate cancer and improve outcomes for men affected by this disease.
Preventing Prostate Cancer: Strategies for Men’s Health and Wellness
Prostate cancer is a significant health concern for men worldwide, but fortunately, there are proactive steps individuals can take to reduce their risk and promote overall well-being. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, undergoing regular screenings, and staying informed about risk factors, men can empower themselves to lower their chances of developing prostate cancer. Let’s explore effective strategies for preventing prostate cancer and promoting men’s health.

Prostate Cancer
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet:
Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Incorporate foods high in antioxidants, such as tomatoes, berries, and cruciferous vegetables, which may have protective effects against cancer. Limit intake of red and processed meats, as well as high-fat and sugary foods, which may increase cancer risk.
2. Stay Active:
Regular physical activity not only supports overall health but may also lower the risk of prostate cancer. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous wdbos activity each week. Along with muscle-strengthening exercises at least twice a week. Incorporate activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, swimming. Or weightlifting into your routine to stay active and maintain a healthy weight.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Obesity and excess body fat have been linked to an increased risk of prostate. Strive to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of nutritious eating and regular exercise. Aim for a body mass index (BMI) within the healthy range (18.5 to 24.9) and avoid excessive weight gain, particularly around the waistline.
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption has been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. Limit intake to no more than two alcoholic drinks per day for men, and consider reducing or abstaining from alcohol altogether to lower your risk. Choose non-alcoholic beverages such as water, herbal tea, or sparkling water as alternatives.
5. Don’t Smoke:
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of several types of cancer, including prostate cancer. If you smoke, seek support and resources to quit smoking and improve your overall health.
6. Get Regular Screenings:
Early detection is crucial for effectively managing prostate and improving treatment outcomes. Men should undergo regular screenings for prostate cancer. Typically starting at age 50, or earlier for those at higher risk due to factors such as family history or African American descent. Screening may involve a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. Which can help detect prostate in its early stages when treatment is most effective.
7. Stay Informed and Advocate for Your Health:
Stay informed about prostate risk factors, screening guidelines, and treatment options. Participate in community outreach and awareness efforts to promote men’s health and encourage others to prioritize preventive care.
Conclusion:
Prostate cancer prevention begins with adopting healthy lifestyle habits, staying active. Maintaining a balanced diet, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco use. By taking proactive steps to reduce risk factors and undergo regular screenings. Men can empower themselves to protect their health and well-being.
Read More Article About “Nature Therapy: Embracing the Healing Power of the Outdoors“



